@
MarmeeMarch says
You do realize it takes energy to recycle anything - right ?
Shockingly, when people calculate lifetime energy usage and lifetime carbon footprint, they take all that into account. I've put an example below.
testing new materials including Lithium
Lithium is new?? Lithium has been used in aerospace aluminum alloys for decades. Lithium has been used in ceramics and glazes for centuries!
Electric cars have a FAR lower lifetime CO2 footprint and a FAR lower lifetime energy footprint. Since energy correlates closely to dollars, it means electric cars have a far lower total cost of ownership.
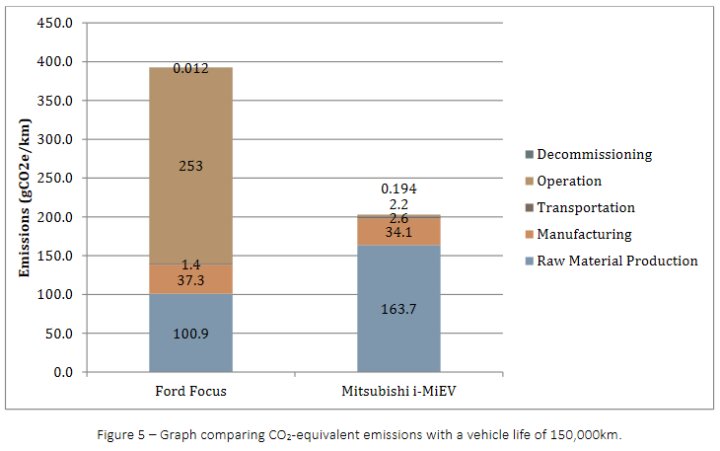
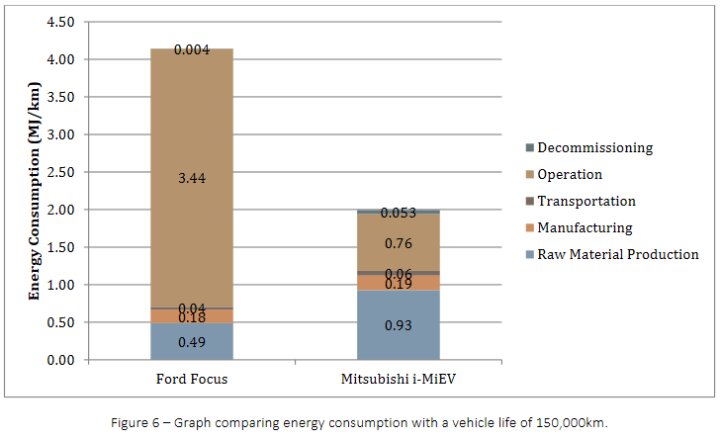
These graphs are for Vancouver CA in 2018, so energy costs are similar to the US; however energy is represented in megajoules - there are 3.6 MJ in a KWH, and 1 MJ = .37 horsepower hours. It assumes 150,000Km of travel over the life of the car, about 93,000 miles.
Lifecycle CO2 costs (these include extracting & transporting oil)
Lifecycle energy costs
Source:
https://sustain.ubc.ca/sites/default/files/2018-63%20Lifecycle%20Analysis%20of%20Electric%20Vehicles_Kukreja.pdfAnd yes, the US has the electric capacity. Now.
If all US cars were EVs, they would need a total of 1,106.6TWh, which is 27.6% of what the American grid produced in 2020.
https://www.forbes.com/sites/jamesmorris/2021/11/13/electricity-grids-can-handle-electric-vehicles-easily--they-just-need-proper-management/
Is There Enough Electricity for EVs? Yes. Here’s Who Will Charge Them.
https://www.barrons.com/articles/theres-enough-electricity-in-the-world-for-electric-vehicles-heres-who-will-charge-them-51605368406
The world has 8,000 gigawatts of installed electricity generation capacity, according to the International Energy Agency. In theory, if the capacity ran 24-7 it could generate 69 million gigawatt hours of electricity annually.
The world consumed about 27 million gigawatt hours of electricity in 2019. That electricity warmed homes and ran businesses. What’s more, the world consumed the equivalent of roughly 28 million gigawatt hours of electrical energy to power its cars and trucks. That energy, of course, was stored in liquid fuel. Power plants didn’t have to generate it. Gasoline and diesel make most of the world’s vehicles go.
So 27 plus 28 is 56. The world needs 56 million gigawatt hours to keep the lights on as well as drive cars and trucks. There is 69 million gigawatt hours of capacity.No problem. But the generating capacity of wind and solar, of course, can’t be “on” 100% of the time. And even coal, nuclear, and hydro power plants have to take maintenance downtime. Still, there looks to be some spare generating capacity and the world’s 2 billion or so vehicles won’t convert to battery power all at once.